James Carter
Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs): A Game-Changing Innovation
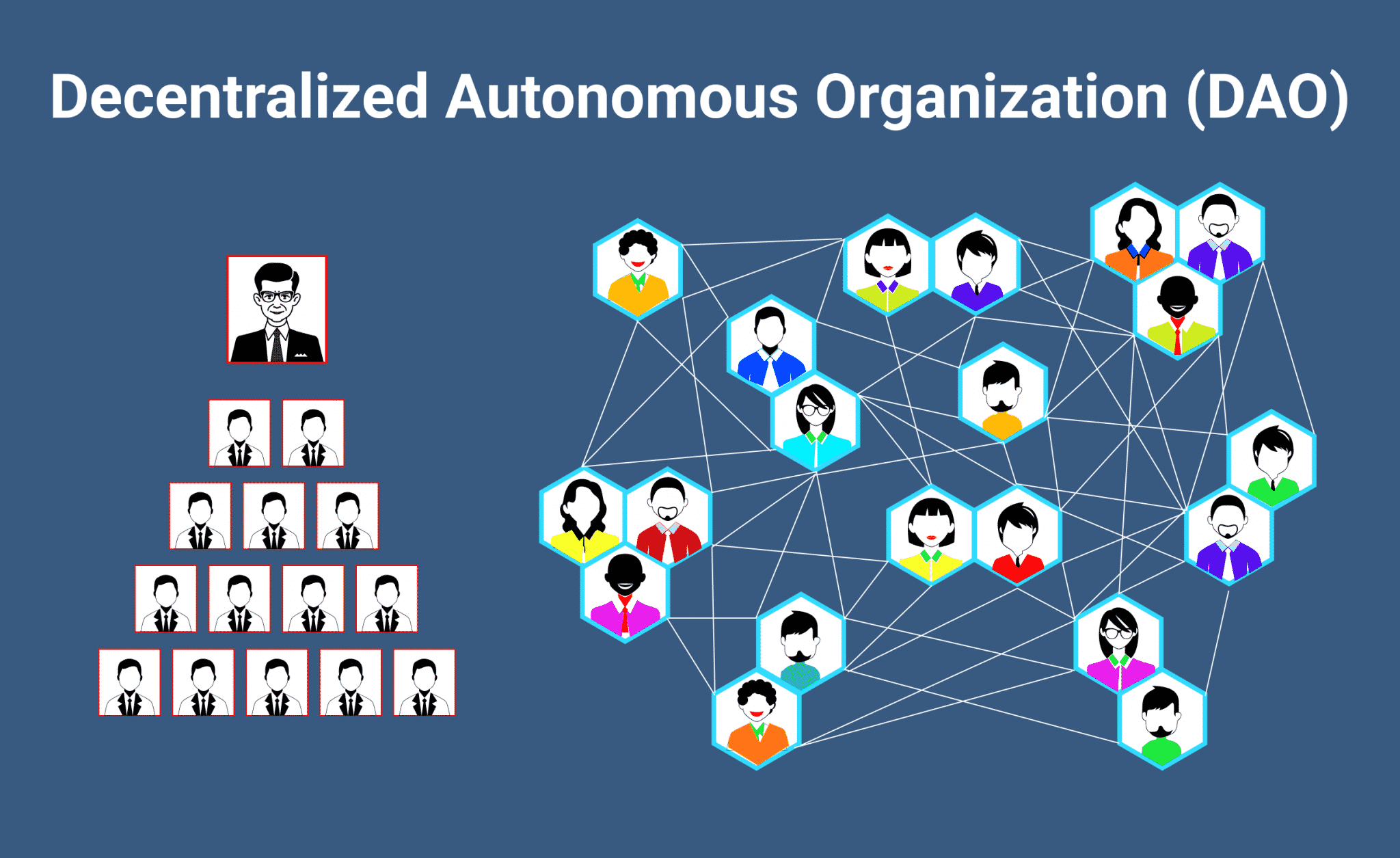
DAOs, or Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, are relatively new concepts in the world of blockchain and cryptocurrencies. These organizations operate using smart contracts and blockchain technology, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as banks, governments, or other centralized authorities. In this article, we will explain what DAOs are, how they work, and their advantages, and provide some examples of existing DAOs.
What are Decentralised Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)?
A DAO is a decentralized autonomous organization that operates using blockchain technology and smart contracts. DAOs are controlled by their members, who make decisions using a voting system built into the DAO’s software. DAOs are often created to serve a specific purpose, such as managing a decentralized platform, investing in cryptocurrency, or distributing funds to a community
1. How Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs) work
DAOs are built on a decentralized network, such as Ethereum, that uses smart contracts to execute predefined rules and operations. These smart contracts are programmed to manage the DAO’s resources, assets, and decision-making processes. The DAO’s members, who hold tokens representing their stake in the organization, can vote on proposals and make decisions collectively. Once a decision is reached, the smart contract executes the outcome automatically.
2. Advantages of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs)
DAOs have several advantages over traditional organizations, including:
A. Decentralization: DAOs operate on a decentralized network, which means that they are not controlled by a central authority or government. This makes them more resistant to censorship, corruption, and other types of interference.
B. Transparency: DAOs are transparent by design, as all transactions and decisions are recorded on the blockchain. This creates a high level of accountability and trust among members.
C. Efficiency: DAOs are highly efficient, as all operations are automated and executed by smart contracts. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces transaction costs.
D. Community involvement: DAOs are created and managed by their members, who have a stake in the organization’s success. This creates a strong sense of community and collaboration among members.
3. Examples of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs)
There are several existing DAOs that serve different purposes, including:
A. MakerDAO: MakerDAO is a decentralized lending platform that allows users to borrow and lend cryptocurrency using stablecoins. The platform is managed by its members, who hold Maker tokens that represent their stake in the organization.
B. MolochDAO: MolochDAO is a community-run DAO that invests in Ethereum-based projects. The organization is funded by its members, who vote on proposals and allocate funds accordingly.
C. DAOstack: DAOstack is a platform for creating and managing DAOs. The platform provides tools for decentralized decision-making, proposal creation, and token issuance.
D. Aragon: Aragon is a platform for creating and managing decentralized organizations. The platform allows users to create DAOs using customizable templates and provides tools for managing proposals, voting, and decision-making.
How do Decentralised Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) work?
1. Decentralization
Decentralization is one of the key features of DAOs. By operating on a decentralized network, DAOs are not controlled by a central authority or government. This makes them more resistant to censorship, corruption, and other types of interference.
DAOs are typically built on blockchain technology, which provides a secure and transparent way to manage transactions and data. The blockchain is maintained by a network of nodes, each of which has a copy of the blockchain. This creates a decentralized system that is resistant to hacking and other types of attacks.
2. Voting and decision-making
DAOs rely on a voting system to make decisions. Members of the DAO can submit proposals, which are then voted on by other members. The voting process is typically conducted using the DAO’s native token, which represents a member’s stake in the organization. The number of tokens held by a member determines their voting power.
Once a proposal is submitted, it is evaluated by the members of the DAO. Members can ask questions, provide feedback, and suggest modifications to the proposal before voting begins. Once the voting period begins, members can cast their vote using their tokens. The proposal is accepted if it receives a majority of the votes.
Smart contracts are used to execute the outcome of the vote automatically. For example, if the proposal is to allocate funds to a specific project, the smart contract will transfer the funds to the designated wallet address once the proposal is accepted.
3. Tokenization
Tokenization is a process in which a digital asset, such as a membership stake in a DAO, is represented by a token on a blockchain. DAOs typically issue tokens to their members, which represent their stake in the organization. These tokens can be bought, sold, or traded on cryptocurrency exchanges.
Tokenization provides several benefits to DAOs. First, it allows members to have a stake in the organization without having to physically own shares or assets. Second, it allows DAOs to raise funds by selling their tokens to investors. Finally, it provides a transparent and secure way to manage membership and ownership of the organization.
4. Smart contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. In the context of DAOs, smart contracts are used to manage the organization’s resources, assets, and decision-making processes.
Smart contracts are programmed with a set of predefined rules and conditions, which are executed automatically when certain criteria are met. For example, a smart contract can be programmed to automatically transfer funds to a specific wallet address once a proposal is accepted by the DAO’s members.
Advantages of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs)
- Transparency
DAOs are transparent by design, as all transactions and decisions are recorded on the blockchain. This creates a high level of accountability and trust among members.
Transparency is an essential feature of DAOs, as it ensures that all members have access to the same information and can participate in decision-making processes. Transparency also makes it easier to identify and address issues or discrepancies in the organization.
- Efficiency
DAOs are highly efficient, as all operations are automated and executed by smart contracts. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and reduces transaction costs.
By eliminating intermediaries, DAOs can operate more efficiently and cost-effectively than traditional organizations. DAOs can also execute operations automatically, without the need for manual intervention, which further increases efficiency.
- Decentralization
Decentralization is a key feature of DAOs, as it eliminates the need for centralized authorities or intermediaries. This makes DAOs more resistant to censorship, corruption, and other types of interference.
Decentralization also provides greater control and ownership to members of the DAO. Members have a stake in the organization’s success and can participate in decision-making processes, which creates a stronger sense of community and collaboration.
- Community involvement
DAOs are created and managed by their members, who have a stake in the organization’s success. This creates a strong sense of community and collaboration among members.
Community involvement is essential for the success of DAOs, as it ensures that members are invested in the organization’s goals and objectives. Community involvement also creates a sense of ownership and accountability, which can lead to better decision-making and more effective management of the organization.
Examples of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs)
- MakerDAO
MakerDAO is a decentralized lending platform that allows users to borrow and lend cryptocurrency using stablecoins. The platform is managed by its members, who hold Maker tokens that represent their stake in the organization. Members can propose changes to the platform and vote on them using their Maker tokens.
- MolochDAO
MolochDAO is a community-led funding platform that supports Ethereum-based projects. Members of the DAO can propose projects and vote on which projects to fund using Moloch tokens, which represent their stake in the organization.
- DAOstack
DAOstack is a platform that enables the creation and management of decentralized organizations. It provides a suite of tools for DAO creation, proposal submission, voting, and execution. DAOstack also provides a reputation system, which allows members to earn reputation points based on their contributions to the organization.
- Aragon
Aragon is a platform for creating and managing decentralized autonomous organizations. It provides a suite of tools for DAO creation, proposal submission, voting, and execution. Aragon also includes a built-in token issuance platform, which allows DAOs to issue their own tokens.
WATCH THE VIDEO BELOW FOR MORE CLARIFICATIONS
Challenges of Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAOs)
Legal and regulatory challenges
DAOs operate in a legal gray area, as they are not recognized by most governments. This can create legal and regulatory challenges for DAOs, especially when it comes to issues such as taxation, securities regulation, and liability.
DAOs may also face challenges in terms of compliance with anti-money laundering and know-your-customer regulations, which can limit their ability to operate in certain jurisdictions.
Governance challenges
DAOs rely on their members to make decisions and manage the organization. However, not all members may have the same level of expertise or commitment, which can lead to governance challenges.
Governance challenges can include issues such as voter apathy, low participation rates, and conflicts of interest. DAOs may need to implement measures to encourage participation and ensure that decision-making processes are fair and transparent.
Technical challenges
DAOs rely on blockchain technology and smart contracts to operate. However, blockchain technology is still in its early stages, and there are many technical challenges that need to be addressed.
Technical challenges can include issues such as scalability, interoperability, and security. DAOs may need to work with developers and technology experts to address these challenges and ensure that their platforms are robust and secure.
Summary
Decentralized autonomous organizations represent an innovative and exciting new way of organizing and managing businesses and communities. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and tokenization, DAOs can operate more efficiently, transparently, and democratically than traditional organizations.
While DAOs still face challenges, such as legal and regulatory hurdles, governance issues, and technical challenges, they hold great promise for the future. As blockchain technology continues to evolve and more people become familiar with the concept of decentralized autonomous organizations, we can expect to see more innovative and impactful DAOs emerge in the coming years.
Latest
Guides & Tutorials
09 May 2024
Guides & Tutorials
19 Apr 2024
Guides & Tutorials
16 Jan 2024
Guides & Tutorials
31 Aug 2023
Guides & Tutorials
24 Jun 2023
Guides & Tutorials
24 Jun 2023













