James Carter
Centralized vs Decentralized Networks: Comprehensive Comparison
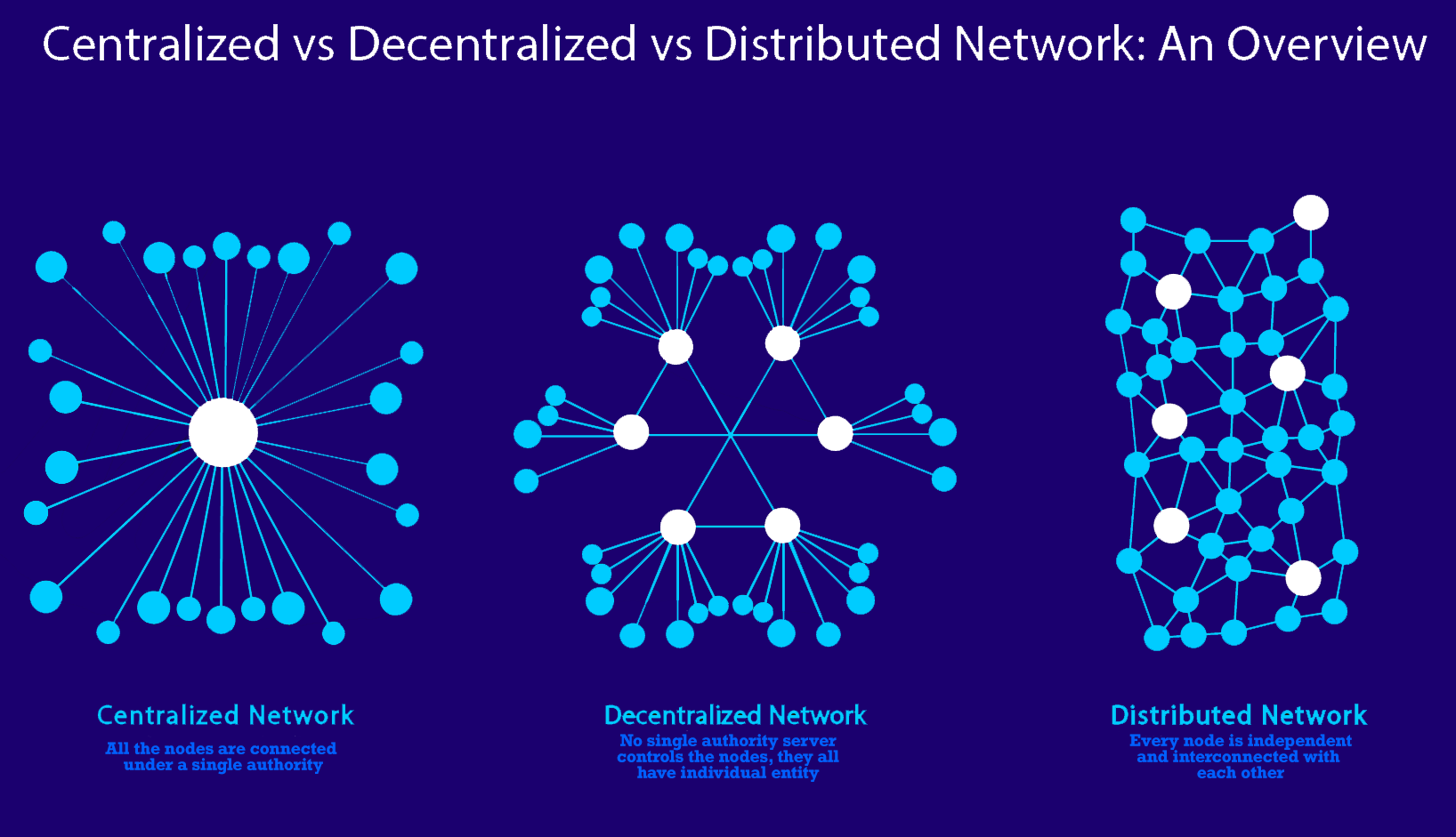
In today’s increasingly digital world, networks play a crucial role in enabling communication, data sharing, and access to resources. However, not all networks are created equal, and it’s essential to understand the differences between centralized and decentralized networks. In this article, we’ll look at what each type of network is like, how it works, what its pros and cons are, and what its future looks like.
I. Centralized vs Decentralized Networks
A. Definition of Centralized and Decentralized Networks
In a centralized network, a single entity or group controls all the resources, decision-making, and communication within the network. On the other hand, a decentralized network is distributed across multiple nodes or participants, with no single entity controlling the entire network.
B. Importance of understanding the differences between the two
Understanding the differences between centralized and decentralized networks is crucial for several reasons. First, it enables us to make informed decisions about which type of network is suitable for a specific use case. Second, it allows us to assess the advantages and disadvantages of each type of network and weigh them against our needs. Finally, it helps us anticipate the potential future developments in network architecture and design.
C. Thesis statement
In this article, we’ll take a close look at centralized and decentralized networks, including how they work, what their pros and cons are, how they can be used, and what the future holds for them.
II. Centralized Networks
A. Definition
A centralized network is a network architecture where all the resources, decision-making, and communication flow through a single entity or group.
B. Characteristics
One of the main characteristics of centralized networks is that they are highly centralized, with all resources and decision-making concentrated in a single entity or group. This architecture allows for a clear chain of command and centralized control of the network. In addition, centralized networks tend to be highly efficient, as they can quickly process data and execute decisions.
C. Advantages
One of the main advantages of centralized networks is their efficiency. Because all the resources and decision-making are centralized, it’s possible to achieve a high level of coordination and control over the network’s operations. This architecture is suitable for applications that require high levels of security and reliability, such as financial transactions, national security, and critical infrastructure.
Another advantage of centralized networks is their scalability. Because all the resources and decision-making are centralized, it’s easier to add new nodes and expand the network’s capabilities. This makes centralized networks suitable for applications that require a high degree of scalability, such as cloud computing, data centers, and large-scale e-commerce platforms.
D. Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of centralized networks is their vulnerability to attack. Because all the resources and decision-making are centralized, a single point of failure can cause the entire network to collapse. In addition, centralized networks are susceptible to censorship and control by a single entity or group, which can lead to abuse of power and violations of privacy and freedom of speech.
Another disadvantage of centralized networks is their lack of innovation. Because all the decision-making and resources are centralized, it’s difficult for new ideas and technologies to emerge and disrupt the status quo.
E. Examples
Examples of centralized networks include traditional banking systems, government agencies, and large corporations.
III. Decentralized Networks
A. Definition
A decentralized network is a network architecture where resources, decision-making, and communication flow through multiple nodes or participants, with no single entity controlling the entire network.
B. Characteristics
One of the main characteristics of decentralized networks is their lack of a single point of control. This architecture allows for a high degree of decentralization and distribution of power, with each node having a certain degree of autonomy and decision-making capability. In addition, decentralized networks tend to be highly resilient in the face of attacks or failures, as there is no single point of failure that can cause the entire network to collapse.
C. Advantages
One of the main advantages of decentralized networks is their resilience and security. Because the network is distributed across multiple nodes, it’s much harder for attackers to compromise the entire network. In addition, decentralized networks allow for greater privacy and freedom of speech, as there is no single entity or group controlling the entire network.
Another advantage of decentralized networks is their innovation potential. Because the network is distributed, it’s easier for new ideas and technologies to emerge and gain traction, leading to greater innovation and progress in the long run. Decentralized networks also tend to be more transparent and open, allowing for greater collaboration and sharing of knowledge.
D. Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages of decentralized networks is their lack of efficiency. Because decision-making and resources are distributed, it can be challenging to achieve a high degree of coordination and control over the network’s operations. In addition, decentralized networks can be less scalable than centralized networks, as adding new nodes can lead to increased complexity and reduced performance.
Another disadvantage of decentralized networks is their complexity. Because the network is distributed, it can be challenging to design and maintain, requiring a high degree of technical expertise and resources. This can make decentralized networks less accessible to the general public and limit their potential applications.
E. Examples
Examples of decentralized networks include blockchain networks, peer-to-peer file-sharing networks, and social media platforms like Mastodon.
WATCH THE VIDEO BELOW FOR MORE CLARIFICATION
IV. Comparison between Centralized and Decentralized Networks
A. Control
Centralized networks offer a high degree of control to a single entity or group, allowing for efficient decision-making and resource allocation. Decentralized networks offer a distributed and shared control model, allowing for greater autonomy and collaboration among participants.
B. Security
Centralized networks are vulnerable to attacks and single points of failure, while decentralized networks are more resilient and secure due to their distributed nature. Decentralized networks also offer greater privacy and freedom of speech, as there is no single entity controlling the entire network.
C. Scalability
Centralized networks tend to be more scalable than decentralized networks, as adding new nodes is easier and can lead to increased efficiency. Decentralized networks can be more challenging to scale due to their distributed nature and increased complexity.
D. Efficiency
Centralized networks tend to be more efficient than decentralized networks, as decision-making and resource allocation can be more streamlined and centralized. Decentralized networks can be less efficient due to their distributed nature, leading to increased complexity and reduced performance.
E. Innovation
Decentralized networks tend to be more innovative than centralized networks, as they allow for greater collaboration and sharing of ideas among participants. Centralized networks can be less innovative due to their concentrated control and potential resistance to change.
V. Applications of Centralized and Decentralized Networks
A. Industries that utilize Centralized Networks
Centralized networks are suitable for industries that require high levels of security and reliability, such as finance, government, and critical infrastructure. They are also suitable for applications that require a high degree of scalability, such as cloud computing, data centers, and e-commerce platforms.
B. Industries that utilize Decentralized Networks
Decentralized networks are suitable for industries that require a high degree of privacy and freedom of speech, such as social media, journalism, and activism. They are also suitable for applications that require a high degree of transparency and openness, such as supply chain management and voting systems.
C. Comparison of the two in terms of suitability for different industries
The suitability of centralized and decentralized networks for different industries depends on several factors, including the level of security, scalability, efficiency, and innovation required. In general, centralized networks are more suitable for industries that require a high level of security and reliability, while decentralized networks are more suitable for industries that require a high degree of privacy, freedom of speech, and innovation.
For example, a bank or financial institution would likely use a centralized network to ensure the security and reliability of their transactions and data. On the other hand, a social media platform or messaging app would likely use a decentralized network to ensure the privacy and freedom of speech of its users.
VI. Future of Centralized and Decentralized Networks
A. Trends
The trend in recent years has been towards greater decentralization, with the rise of blockchain technology and decentralized finance (DeFi) leading the way.
B. Challenges
One of the main challenges facing decentralized networks is their complexity and scalability. As more nodes are added to the network, it becomes increasingly challenging to maintain and scale, leading to reduced performance and efficiency. In addition, decentralized networks face regulatory and legal challenges in some jurisdictions, which could limit their adoption and growth.
C. Potential Solutions
To address these challenges, researchers and developers are exploring new solutions such as sharding, layer-two scaling solutions, and improved governance models. These solutions aim to improve the scalability, efficiency, and governance of decentralized networks, making them more accessible and suitable for a wider range of applications.
Summary
Centralized and decentralized networks represent two fundamentally different approaches to network architecture, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Centralized networks offer a high degree of control and efficiency, while decentralized networks offer resilience, security, and innovation.
The choice between centralized and decentralized networks depends on the specific needs and requirements of a given industry or application. In general, centralized networks are more suitable for industries that require a high level of security and reliability, while decentralized networks are more suitable for industries that require a high degree of privacy, freedom of speech, and innovation.
As technology advances and new solutions are developed, the boundaries between centralized and decentralized networks are likely to become increasingly blurred. Ultimately, the future of networking is likely to be a hybrid model that combines the best aspects of both centralized and decentralized networks to create a more efficient, secure, and innovative network architecture.
Latest
Technology
21 Feb 2026
Technology
13 Feb 2026
Technology
07 Feb 2026
Technology
06 Feb 2026
Technology
05 Feb 2026
Technology
03 Feb 2026












