Coinposters
Decentralized Apps (dApps): Everything to Know
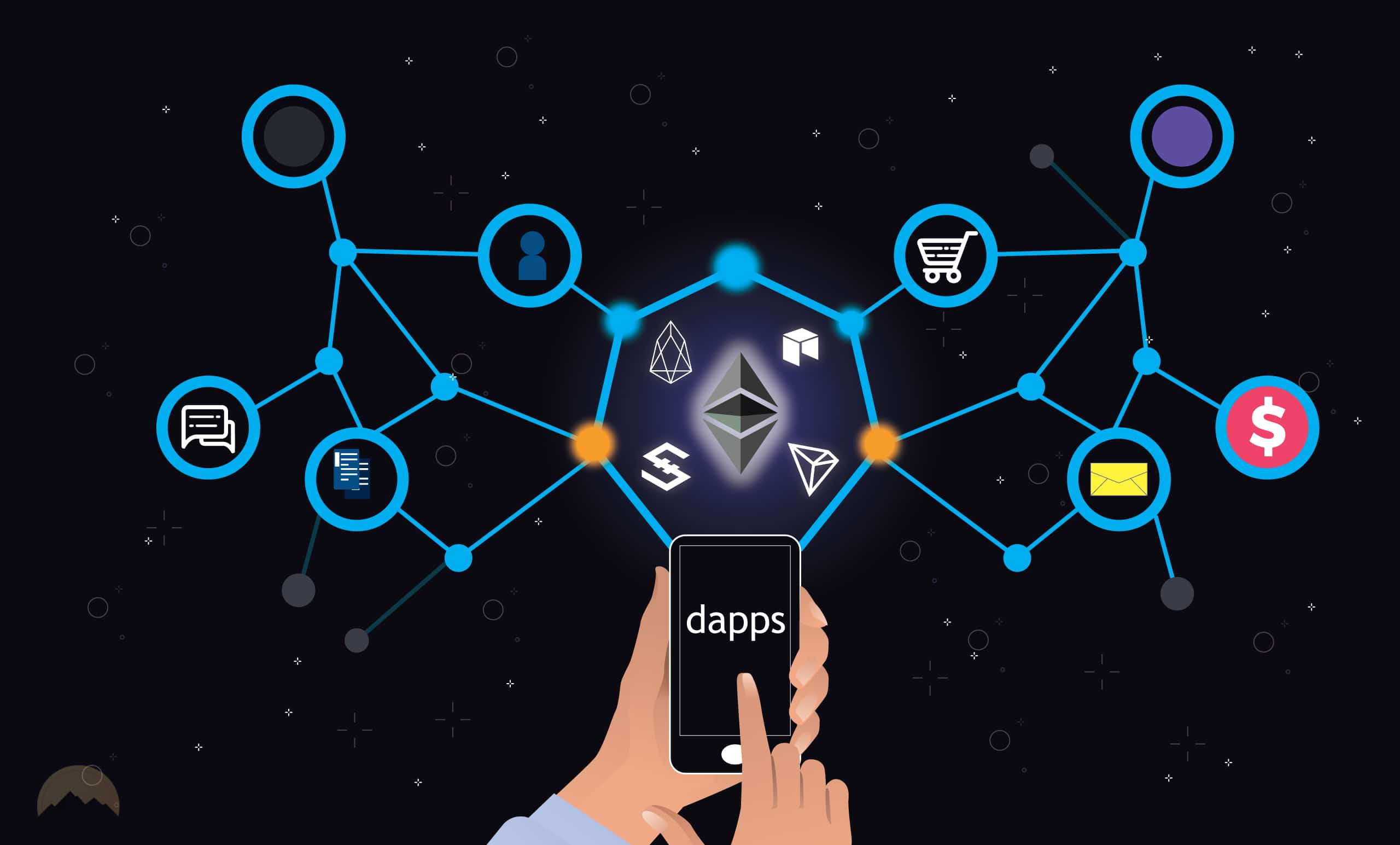
As blockchain technology continues to gain popularity and be used by more organizations, attention is shifting to a specific area that has enormous potential: decentralized applications (dApps).
The authority formerly held by monopolistic businesses is being usurped by decentralized apps, which are spawning a new digital economy based on peer-to-peer service exchanges. Continue reading to learn all you need to know about decentralized apps.
What Are dApps?
Decentralized apps, often known as dApps, are computer programs or applications that are digital in nature and that operate on a blockchain or peer-to-peer (P2P) network of computers rather than on a single computer. Simply put, these are applications that do not fall under the jurisdiction or control of a single authority.
dApps, which are often constructed on the Ethereum platform, have the potential to be created for a wide range of uses, some of which include the gaming industry, the financial sector, and social media.
Dapps are just as diverse as traditional apps; they may include social networks, games, and other forms of entertainment, as well as features that can help users be more productive.
Many are intended as consumer-friendly solutions that provide access to decentralized financial services, often known as DeFi.
The latter function is so pervasive that the white paper for the Ethereum network divided decentralized applications (dapps) into three categories: “financial,” “semi-financial,” and “other.”
History
When Vitalik Buterin and his colleagues first suggested Ethereum (ETH) in 2013, they envisioned an internet based on blockchain technology, one in which people, not companies, would have power.
In order to accomplish this goal, Ethereum would be used to power smart contracts, which are effectively automated if-then statements. These contracts are inflexible since the stipulations and restrictions were included into the source code.
Because of this, any two parties may do business directly with one another, doing away with the need for centralized platforms.
It’s interesting to note that the term “Dapp” wasn’t officially defined until 2014 when a study entitled “The General Theory of Decentralized Applications, Dapps” was published. It was authored by a number of writers, including David Johnston and Shawn Wilkinson, both of whom have previous expertise in the field.
Why dApps?
Users of decentralized applications (dApps) may have more peace of mind if they are aware that the developers of the program do not have the ability to regulate how it is used, at least not in the traditional sense.
For instance, the developers of a decentralized application (dApp) for a social network do not have the authority to delete a post or block a user. They are also unable to sell the data of users to other organizations since decentralized applications operate on their own after they have been published.
How is it that this is even possible? The use of “smart contracts,” which are computer programs that are stored on a blockchain and are meant to carry out the terms of a contract without the intervention of a person, is the key to everything.
For illustration purposes, a smart contract may be programmed to provide a loan only when a user has deposited an adequate quantity of collateral into the contract. Additionally, decentralized applications are often open source, which means that anybody is able to inspect and make use of the underlying code.
In the context of digital currency, decentralized applications (dApps) are applications that operate on a blockchain network inside an open-source, public, and decentralized environment. These applications are immune to control and intervention from any central authority.
A developer, for instance, may construct a decentralized application (dApp) that is similar to Twitter and then place it on a blockchain, where any user could submit messages. After they have been published, the messages cannot be removed by anybody, not even the developers of the program.
Pros
- Defiant against censorship – Because there is no central point of failure, it is very difficult for strong people or governments to exert control over the network.
- There is no downtime – By using a peer-to-peer method, decentralized applications (dApps) will continue to function normally even in the event that certain machines or portions of the network become inoperable.
- Using the blockchain – Since they are constructed using smart contracts, it is simple to include cryptocurrencies into the fundamental capabilities of the decentralized application (dApp).
- Open-source – Open-source decentralized applications incentivize the expansion of the app ecosystem and make it possible for developers to create superior decentralized applications with features that are either more helpful or more fascinating.
Cons
- A leisurely pace – It is possible that certain transactions may be held up during the processing of the decentralized system; as a result, this will add lag time to the operation that is being carried out in the network. Only around 10-15 transactions may be processed by the network per second at most.
- Intensive Care Required – It is just as difficult to edit the code and data that has been published on a blockchain as it is to create a decentralized application (Dapp). Once the Dapps have been launched, it is difficult for developers to make adjustments, even in the event that a flaw is discovered.
- Experience for the end user: As dApps focus on improving efficiency and security, they often overlook the needs of their end users. If this is the case, it might slow down the pace at which people embrace digital technologies in that country.
- Immutable – The immutability of decentralized applications (dApps) is something experts see as a positive, but it may also have drawbacks. For example, smart contracts are created by people, and because mistakes made by humans are inevitable, dApps with this feature have the potential to cause serious issues.
Closing Thoughts
As of right now, Dapps are in their infancy. However, hundreds of dapps currently provide a wide variety of services, including as gaming, DeFi investment, and NFT trading.
dApps, like traditional applications, may open the door to a world of new digital possibilities. They’re now commonplace in banking and social media applications, and they might quickly spread to productivity software, game engines, and marketplaces.
Latest
Guides & Tutorials
25 Feb 2026
Guides & Tutorials
21 Feb 2026
Guides & Tutorials
13 Feb 2026
Guides & Tutorials
07 Feb 2026
Guides & Tutorials
06 Feb 2026
Guides & Tutorials
05 Feb 2026